Types of binoculars
Basic Information about Binoculars
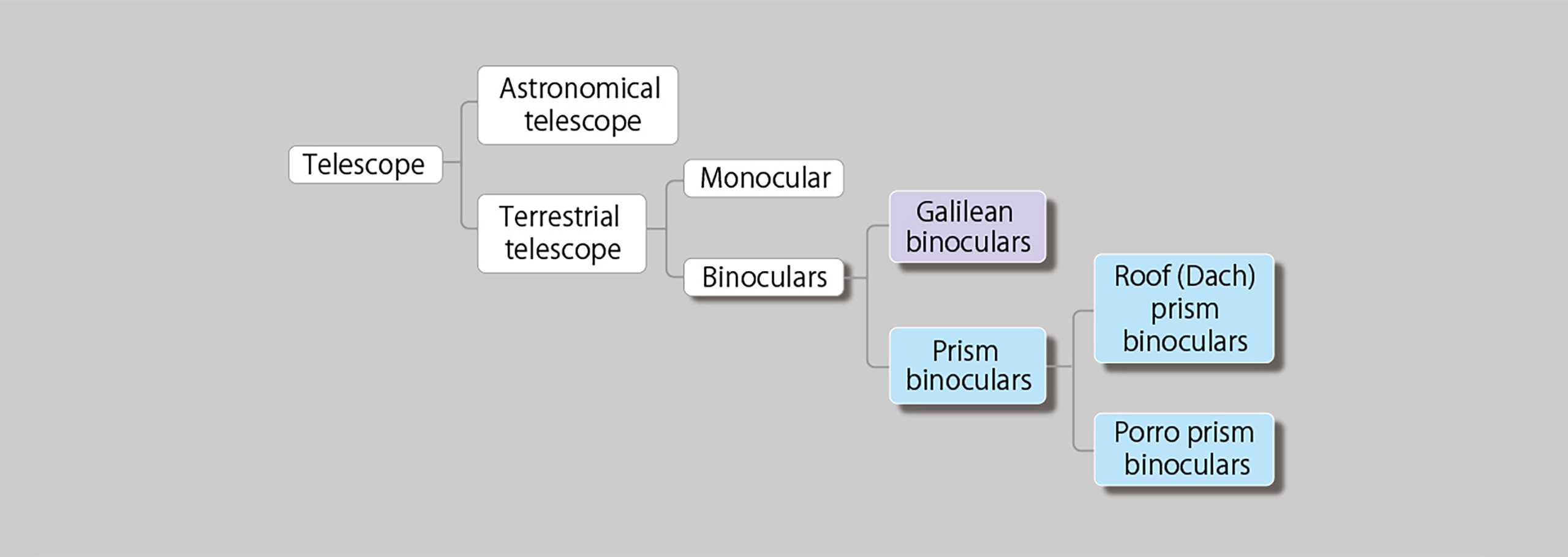
Binoculars are classified as follows:
Differences between astronomical and terrestrial telescopes
An astronomical telescope (Keplerian telescope) uses convex lenses for both objective and eyepiece lenses, and the image is inverted. It is designed to give objective lens optical performance top priority and minimize light loss, so a prism to rectify the image is not incorporated.
A terrestrial telescope incorporates a prism between the objective and eyepiece lenses to rectify the image. It is convenient to observe erect images of landscapes and objects.
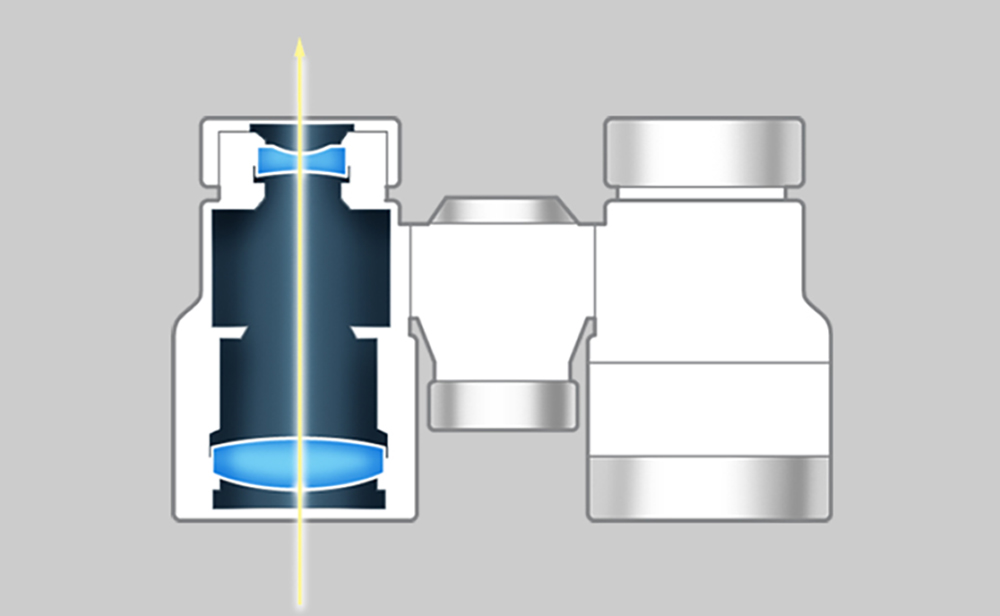
Galilean binoculars
Galilean binoculars are so called because they feature the same structure as that used in the instrument first used by the Italian astronomer Galileo Galilei for astronomical observation in 1609. These binoculars consist of convex lenses for objectives and concave lenses for eyepieces and form erect images.
Because no prism is employed, the binoculars can be made compact and lightweight. However, maximum magnification is up to about 4x. Generally, the field of view is not wide, and the peripheral areas of the field are likely to be out of focus. Opera glasses are usually of this type.
Prism binoculars
Convex lenses are used for both objectives and eyepieces. A wider field of view and high magnification can be attained than is the case with Galilean binoculars. An erecting prism system is incorporated in the optical path to rectify the image. Also, employing prisms has the effect of making the length of such binoculars shorter. There are two types of prism binoculars: Roof (Dach) prism type and Porro prism type.
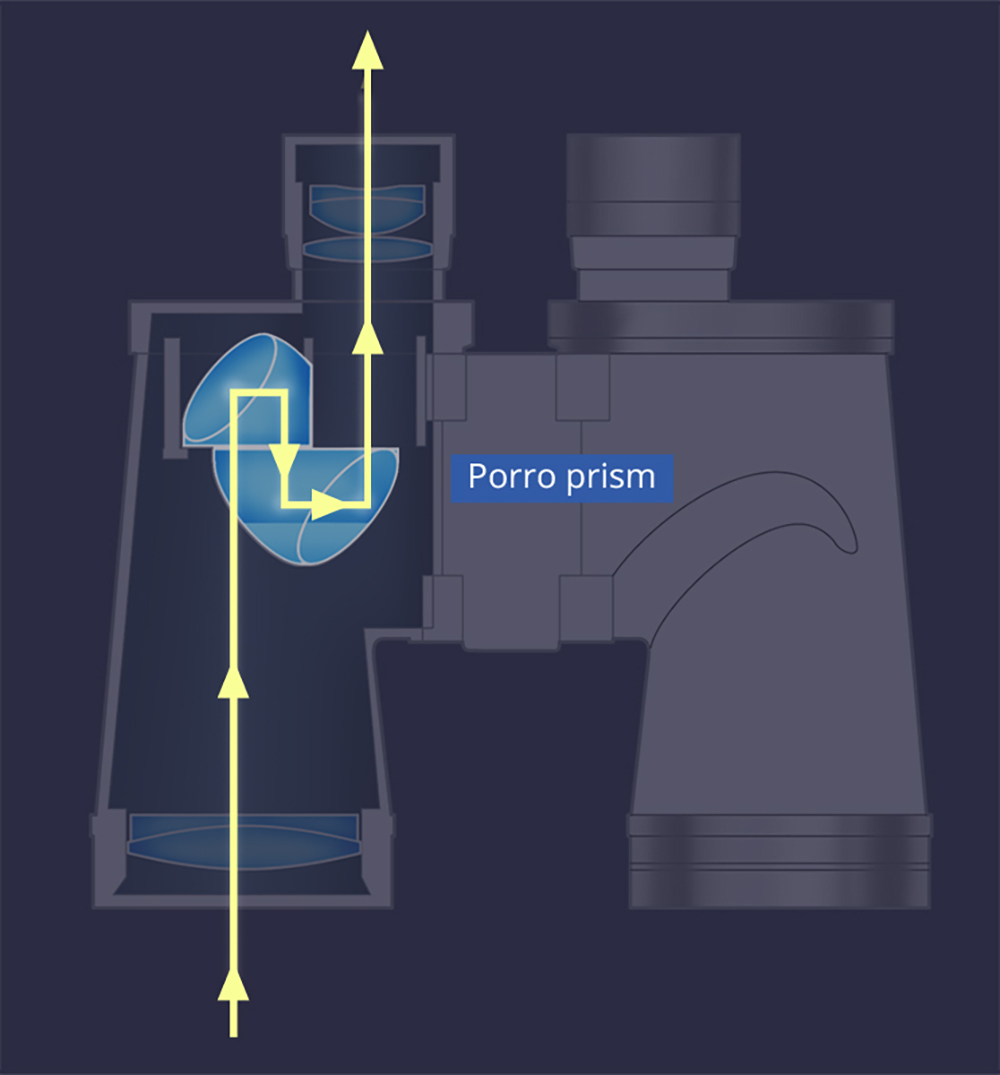
Porro prism binoculars
Porro prism binoculars create an erect image with two prisms (four prisms total with both sides). This was invented by Ignazio Porro in Italy in the middle of the 19th century and has the longest history among prism binoculars.
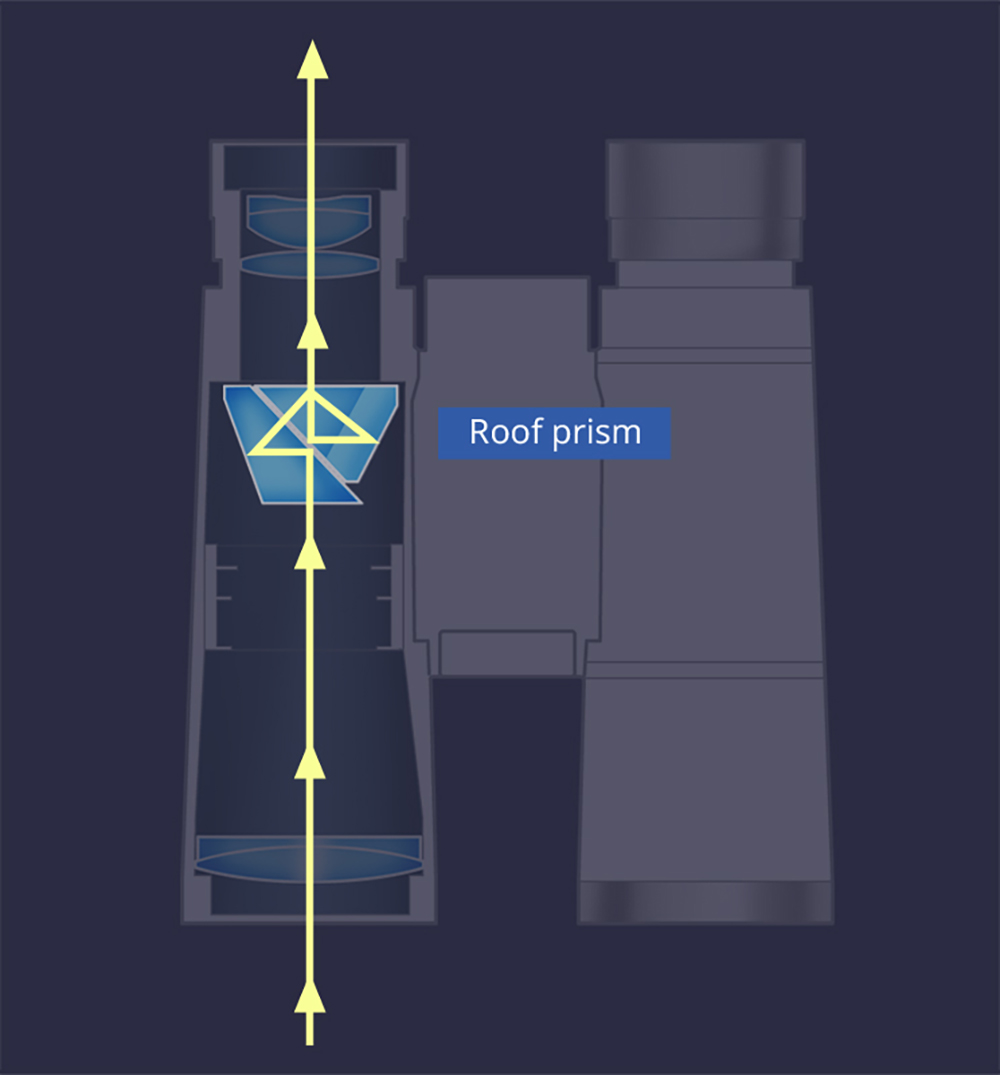
Roof (Dach) prism binoculars
The roof prism system is used to rectify the image for this type of binoculars. "Dach" means roof in German, and this type of prism features a roof-shaped surface. The optical path at the objective side and eyepiece side is virtually straight, making it possible for the binoculars to be compact and lightweight. However, manufacturing and adjusting the prism require very high technology. Demand for this type of binoculars is expected to grow as more customers prefer its slim, stylish design.