NIKKOR - The Thousand and One Nights No.64

EL-Nikkor 80mm f/5.6N
In this Tale, I'd like to talk about something a little different; a NIKKOR lens that is not exactly a photographic lens. That said, it is a lens that is very familiar to those who have enjoyed photography since the film age. The subject of Tale 64 is an EL-Nikkor enlarger lens.
While there is no established theory as to when enlargers and enlarger lenses first came into existence, it seems likely that the need for such devices was recognized, and that they became relatively common around the same time that 35mm cameras from Leica and other manufacturers became popular. Images captured using 4x5 in., 8x10 in., and other large-format cameras were often printed using a method known as contact printing (an exposed and developed piece of film is placed emulsion side down, in contact with photographic paper, light is thrown through the negative, and the paper is developed to reveal the final print), the defining characteristic of which is that the resulting print is the same size as the original. Even contact prints of images captured with 6x9 cm and 6x6 cm medium-format cameras were just large enough for viewing.
However, with 35mm film that has a frame size of just 24x36 mm, contact printing is difficult because the resulting photos are so small that it is often difficult to identify even the primary subject, let alone fine details. Therefore, as 35mm cameras became more and more popular, means of enlarging the photos captured with them were developed.
by Kouichi Ohshita
I. EL-Nikkor history
After WWII, Nippon Kogaku was involved in the development of binoculars, cameras, photographic lenses, and also lenses used in a variety of other fields. Two examples are the Apo-Nikkor and Cine-Nikkor lines of lenses. Apo-Nikkor lenses were used for photoengraving and Cine-Nikkor lenses for cinematic applications. Since enlarger lenses were very well suited to the compact cameras being developed at the time, planning of such a lens at Nippon Kogaku began at an early point in 35mm history with the first 50mm f/3.5 released in 1948 and another faster (brighter) 50mm f/2.8, with which performance had also been increased, released in 1957. This 50mm f/2.8 was well received for its superior performance, and the response at Nippon Kogaku was to present a plan for the EL-Nikkor series, a line of enlarger lenses, in the 1960s. In 1966, the EL-Nikkor 80mm f/5.6, the first lens in the series, was released. The EL-Nikkor series was completed with the additional release of the 63mm f/3.5, 105mm f/5.6, and 135mm f/5.6 in 1966, the 50mm f/4 in 1967, and the 75mm f/4 in 1972.
Once the series was complete, EL-Nikkor lenses were continuously improved.
Around 1980, optical design of EL-Nikkor lenses was modified and a gradual shift to the "N" series, the exteriors of which were changed to take darkroom operation into consideration, was began. In 1980, the 80mm f/5.6 was reborn as the EL-Nikkor 80mm f/5.6N with even better optical performance.

It is, however, ironic that demand for enlargers and enlarger lenses would gradually decrease from that time on. One reason was the increase in the performance of color negative film and the popularity of color photos. I remember that color negative film became popular when I was a child in the 1970s. At that time, color film and prints were much more expensive than their black-and-white counterparts. Even so, their ability to reproduce colors was inferior to that of reversal film. Therefore, it was the common view of advanced amateurs at the time that any commemorative photo or photo to be used as a lasting record had to be taken using black-and-white or reversal film. However, great leaps were soon made with color negative systems so that by the 1980s color reproduction characteristics nearly as good as those of reversal film were possible. I was at university at the time, and I'll never forget the shock I felt the first time I saw a print made from Fujicolor HR film (released in 1983).
The rise of digital cameras was ultimately the end of the enlarger lens.
Enlargers and enlarger lenses were not needed to print images captured with digital cameras. These photos could now be printed using computers and printers. Thus, in 2006, Nikon quietly discontinued sales of its EL-Nikkor series of enlarger lenses so as not to draw attention away from its extremely popular digital cameras, including the Nikon D70 (released in 2004) and D40 (released in 2006).
II. Applications other than just enlargement
Though this Tale has been somewhat dismal thus far, it is important to note that Tochigi Nikon continues to manufacture some EL-Nikkor lenses, including the 50mm f/2.8, for industrial applications. That is because EL-Nikkor lenses have long been incorporated into a variety of devices, serving as their "eyes". While I cannot share specific details, I can point out that the EL-Nikkor 50mm f/2.8, for example, is well known for its use as a projection lens in the Megastar planetarium projector.
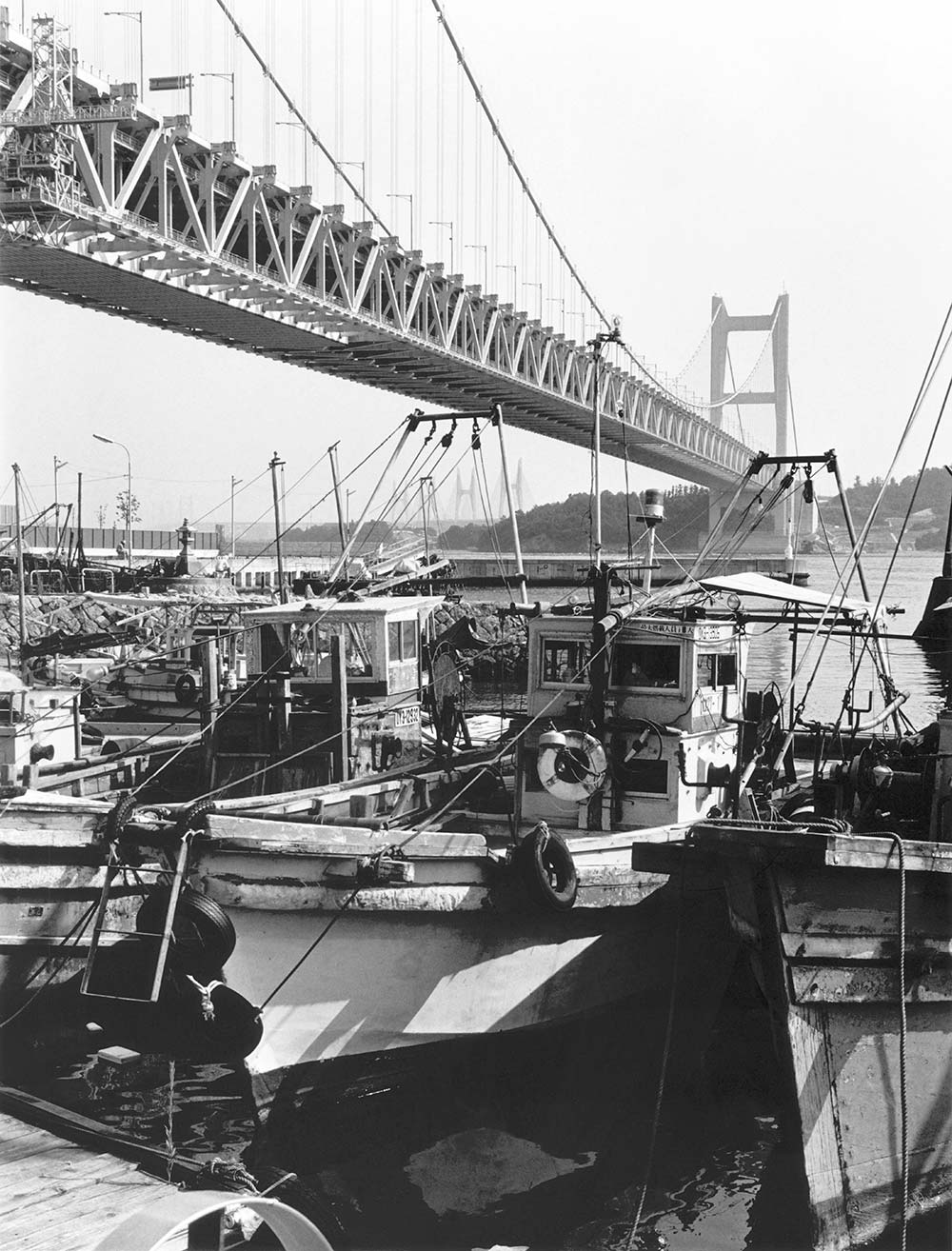

Captured with 6x4.5 cm medium-format camera
(Fujifilm GS645 with 75mm f/3.5 at f/8), Kodak T-MAX400, developed using Super Prodol (SPD) at magnification of 1:1
Enlarged using EL-Nikkor 80mm f/5.6 lens at f/11, printed on photographic paper using SPVR3
In recent years, enlarger lenses have once again taken a place in the limelight as photographic lenses. One reason suggested for this trend is the emergence of mirrorless cameras, which exhibit greater flexibility in terms of back focus than do SLR cameras, but I think there is another.
Sample image 1 was enlarged using the EL-Nikkor 80mm f/5.6N. Because the photo was scanned, resolution is not as high as it could be, but it exhibits consistent sharpness throughout the entire frame. However, this is a characteristic of the photographic lens (and film) used to capture the photo, not a characteristic of the EL-Nikkor used to enlarge it. The primary requirement of an enlarger lens is that it project the original film image as is onto photographic paper. If the enlarger lens exhibited certain characteristics that were projected onto the photo, the lens would be considered a failure as an enlarger lens. The most important principle behind enlarger lenses is that they do not project any unique characteristics they may have. Therefore, I think that people want to use EL-Nikkor lenses as photographic lenses for just this reason. They do not exhibit or project any unique characteristics.
III. The EL-Nikkor 80mm f/5.6N
The new version of the 80mm f/5.6 EL-Nikkor was designed by someone whose name is frequently mentioned in these Tales, Mr. Ikuo Mori. Tasked with coming up with new designs for the EL-Nikkor series, Mr. Mori designed the new ELNikkor 50mm f/2.8N that Haruo Sato briefly introduced in Tale 9, as well as a number of other lenses.
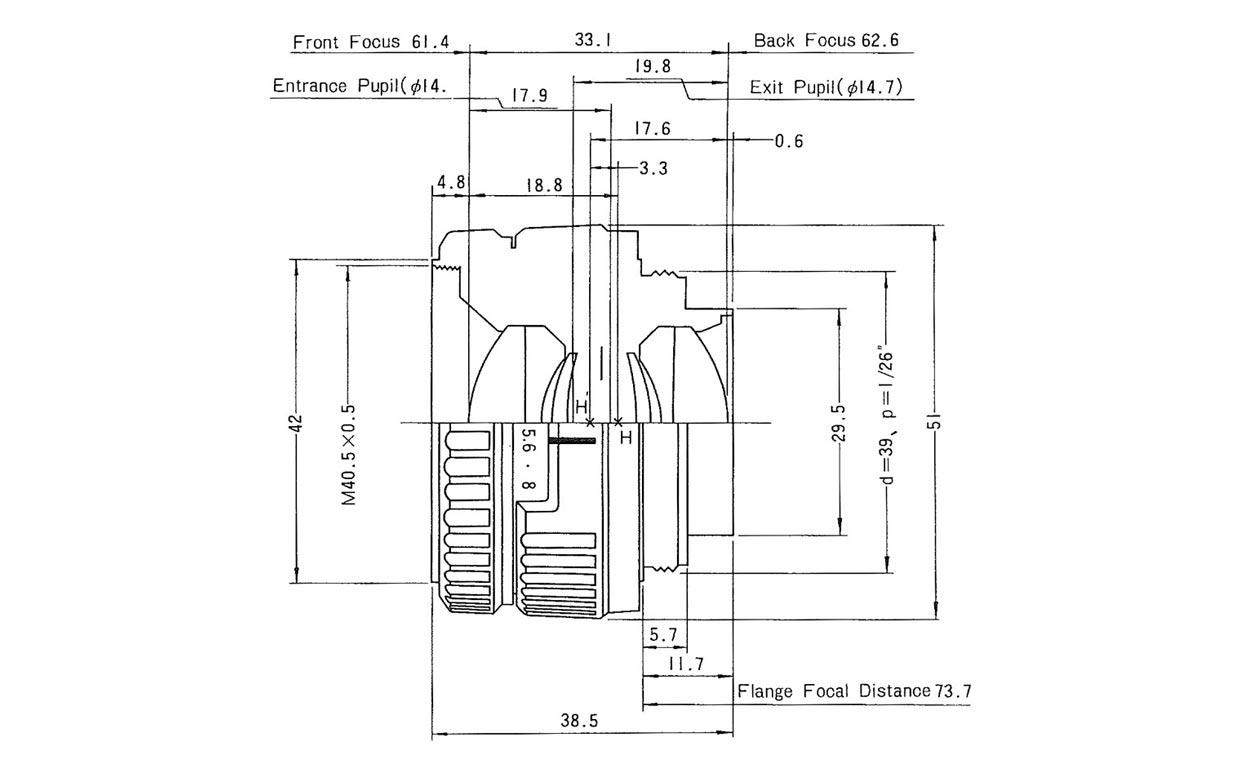
Figure 1 shows how this lens was constructed. The lens is constructed with a meniscus-shaped doublet, made up of one convex and one concave lens element, that faces the convex surface on the object end, a convex meniscuslens element that faces the convex surface on the object end, the aperture, a convex meniscus lens element that faces the convex surface on the imaging (focal plane) end, and a meniscus-shaped doublet, made up of one concave and one convex lens element, that faces the convex surface on the imaging (focal plane) end. Lenses constructed in this manner are known as Orthometartype lenses. While this structure is not commonly used for SLR lenses, it is often used with wide-angle lenses for large-format cameras. As Orthometartype lenses have a symmetrical construction, they offer good compensation for distortion, coma, and lateral chromatic aberration, and superior compensation for curvature of field and astigmatism over broad angles of view. The Orthometar type is also said to be the optimal lens type for enlarger lenses that perform best with a flat field (focal plane). On the other hand, as this type of lens does not offer sufficient compensation for spherical aberration, it is difficult to design fast (bright) Orthometar-type lenses. Therefore, the maximum speed (brightness) of this type of lens is generally around f/5.6.
By the way, just what are the requirements of an enlarger lens? One is its ability
to project the original image onto photographic paper. Standard magnifications were set with the EL-Nikkor series at 8x for 50mm lenses and 5x for 75mm and 80mm lenses. These standards assume enlargement of photos taken using 135 and 120 film to roughly 10 x 12 inches in size. I suppose this is the most definitive difference between enlarger lenses and photographic lenses for which shooting over a broad range of distances, from infinity to close-ups, is assumed.
It is important to note that with use of a magnification range of 2-20x assumed for the EL-Nikkor 50mm, and 2-15x for the 80mm lens, infinity is not included.
Another requirement of enlarger lenses is that they be capable of compensating for aberration over a broader wavelength band that can photographic lenses.
Black-and-white photographic paper, which is considered the standard, is sensitive only to near ultraviolet to violet light. On the other hand, when an enlarger is used, focus is performed by a human being. Therefore, green to yellow focus positions that humans use for focusing and the violet focus position must all be the same. What's more, good aberration compensation throughout the entire visible spectrum is necessary for color enlargements. As a result, EL-Nikkor lenses were designed with consideration of a broad range of wavelengths, from near ultraviolet at 380 nm to near infrared at 700 nm.
Finally, a requirement that cannot be overemphasized, is the ability of enlarger lenses to project images onto photographic paper with the same level of quality and precision as with photographic lenses. Projected images must exhibit no distortion, the field must be flat, there must be no vignetting or peripheral illumination falloff, and resolution must be good. However, the last two items, vignetting and resolution, require good performance not at maximum aperture, but rather at the aperture settings actually used. Enlarger lenses are rarely used at maximum aperture. 50mm lenses are often stopped down to between f/8 and f/11, and 80mm lenses to between f/11 and f/16 to ensure adequate exposure control. However, it is important to remember that stopping down the aperture too much results in diffraction that reduces resolution.
IV. Lens rendering
Let's end this Tale with a look at some sample images captured using the ELNikkor 80mm f/5.6 as the photographic lens. As Figure 1 shows, this lens has a sufficiently long back focus of 62.6 mm and flange focal distance (distance fromthe mount to the focal plane) of 73.7 mm to enable focusing from infinity, even when mounted on an SLR camera. As this lens has the Leica screw mount (L mount) common not only to EL-Nikkor lenses, but most enlarger lenses, an L mount to F mount adapter is required to use the lens with an F-mount camera.
However, as EL-Nikkor lenses are not equipped with focusing mechanisms, a separate mechanism that moves lens elements forward for focusing must be prepared. As there is a lot of forward movement with the 80mm focal length, use of a bellows is convenient if priority will be given to shooting at short distances.
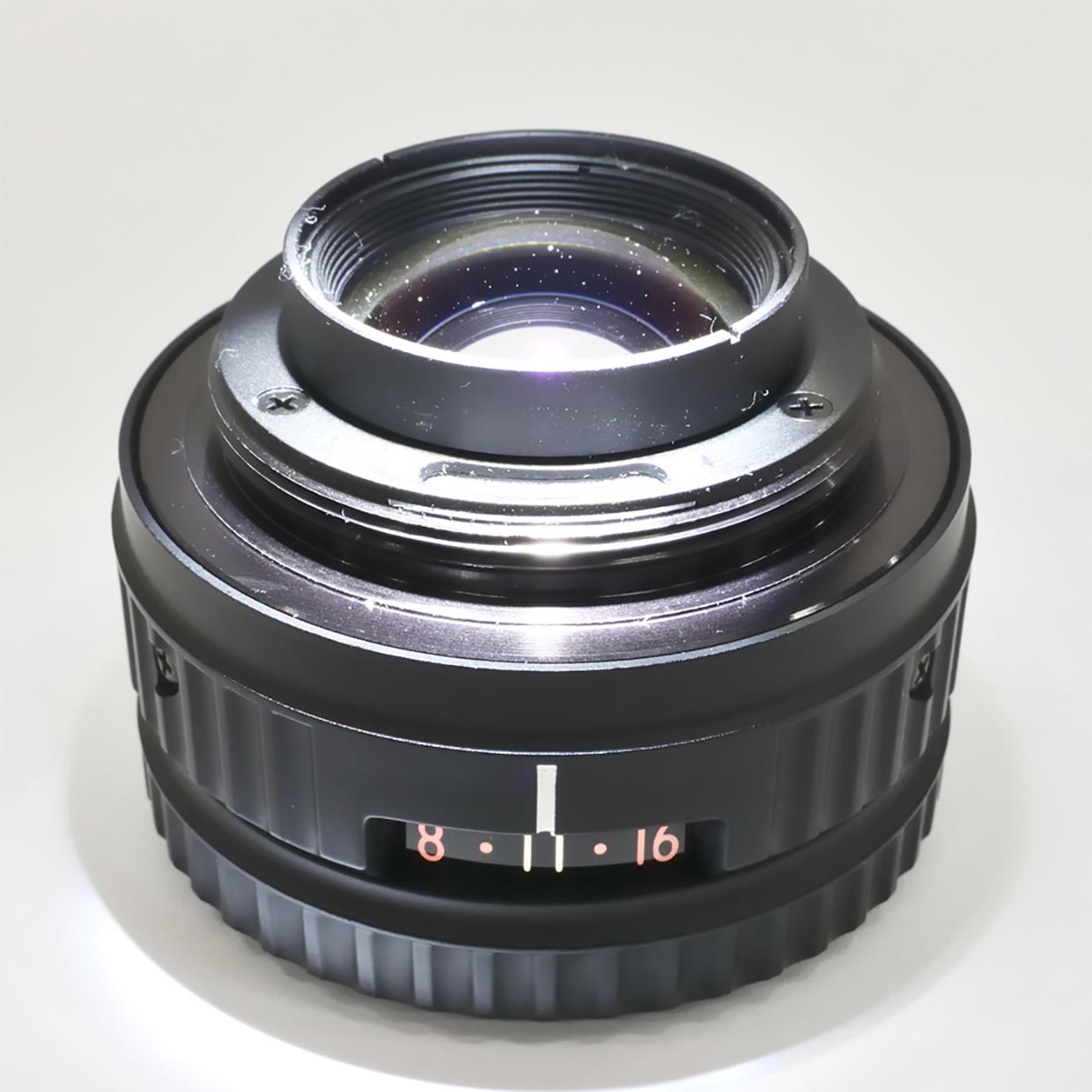
In addition, as Photo 2 shows, N-type EL-Nikkor lenses have a window that lets light through to the aperture value when the lens is mounted on an enlarger.
While this mechanism is very convenient for darkroom work, it causes light leak when used as a photographic lens, and must therefore be covered.
Sample 2 is a photo of Tokyo Station captured at maximum aperture. With a magnification of approximately 1/300x, this photo differs greatly from those achieved with normal use. However, as the image was captured with a 6 x 7 cm medium-format lens and then cropped, it exhibits generally consistent rendering all the way to the extreme corners of the frame. With simulations, some inner coma occurred at frame edges near a distance of infinity, so rendering should be slightly softer in the extreme corners. However, if that is the case, it is hardly noticeable. This lens makes full use of the D810's high pixel count with clear and faithful rendering of even mortar joints.

D810 and EL-Nikkor 80mm f/5.6, f/5.6, ISO 100, aperture-priority auto, processed with Capture NX-D
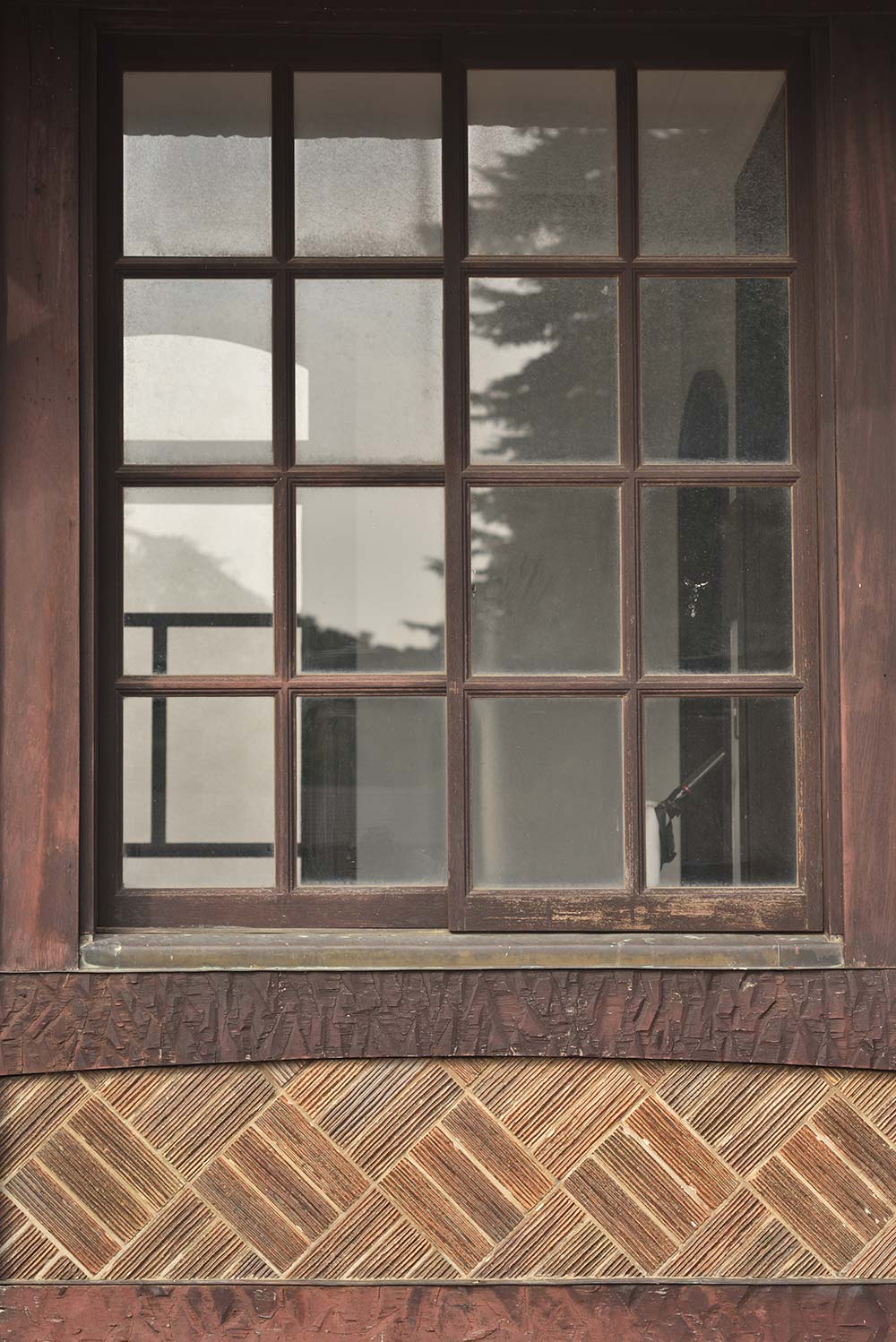

D810 and EL-Nikkor 80mm f/5.6, f/5.6, ISO 100, aperture-priority auto, processed with Capture NX-D

D810 and EL-Nikkor 80mm f/5.6, f/5.6, ISO 400, aperture-priority auto, processed with Capture NX-D
With Sample 3 we get even closer to approximately 1/50x with a photo of an old-fashioned window captured at maximum aperture. The photo exhibits extremely sharp rendering, clearly reproducing even the grain of the wood and the dust on the glass to portray most directly the building's various textures.
Naturally, this enlarger lens produces hardly any distortion, so there is no concern at all that the lines in this photo will be curved in any way.
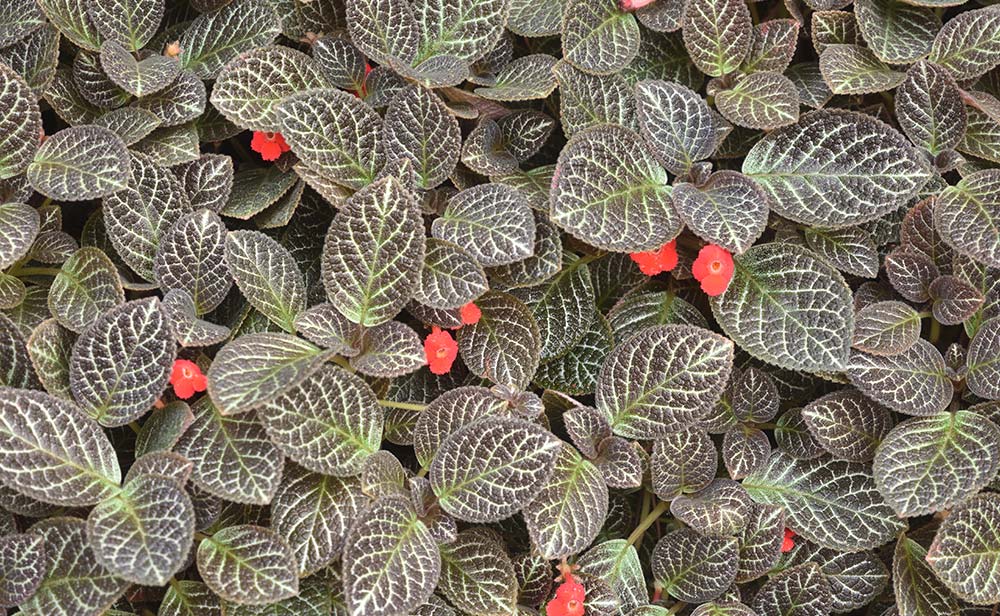
Sample 4 is a photo of plants captured at a distance close to the standard design magnification. As the shooting distance decreases, so does depth of field. Therefore, I wanted to stop down the aperture, but as the photo was taken inside a greenhouse that didn't have room for a tripod, I struggled to get as much of the frame in focus as possible with hand-held shooting at maximum aperture.

D810 and EL-Nikkor 80mm f/5.6, f/5.6, ISO 100, aperture-priority auto, processed with Capture NX-D

D700 and EL-Nikkor 80mm f/5.6, f/11, ISO 200, aperture-priority auto, processed with Capture NX-D

D810 and EL-Nikkor 80mm f/5.6, f/8, ISO 100, aperture-priority auto, processed with Capture NX-D
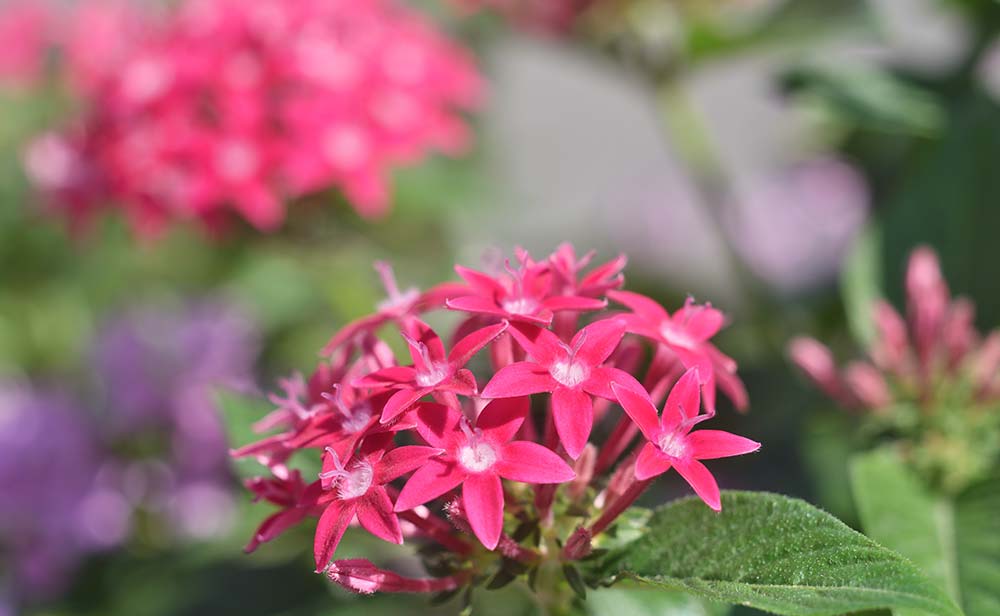
Sample 5 is a photo of a flower captured at a magnification just under 1/3x. As lens zones cause spherical aberration and outer coma with shooting at close distances that exceed the standard magnification, performance drops gradually, but this drop is most noticeable in background blur (bokeh). While in-focus portions are still sharp and clear, background bokeh is not very pleasing, and a little distracting, with its ring shape. The hard-edged bokeh caused by aberration can likely be resolved by stopping down the aperture one or two stops.
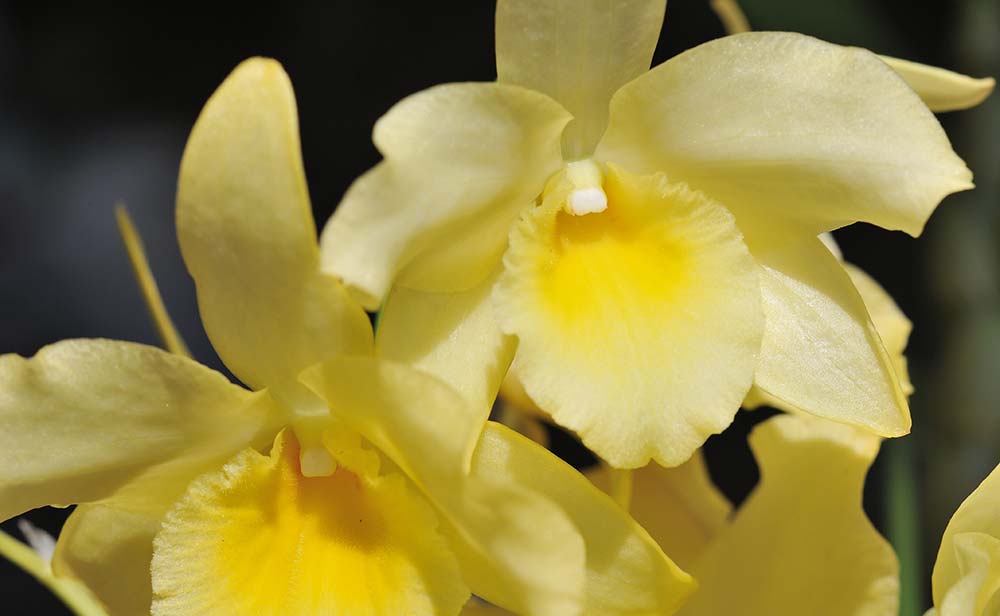
Sample 6 was captured at about the same magnification as Sample 5, but as the subject is a more three-dimensional orchid, I stopped the aperture down to f/11. With the aperture stopped down, the hard-edged bokeh exhibited by Sample 5 has been resolved.
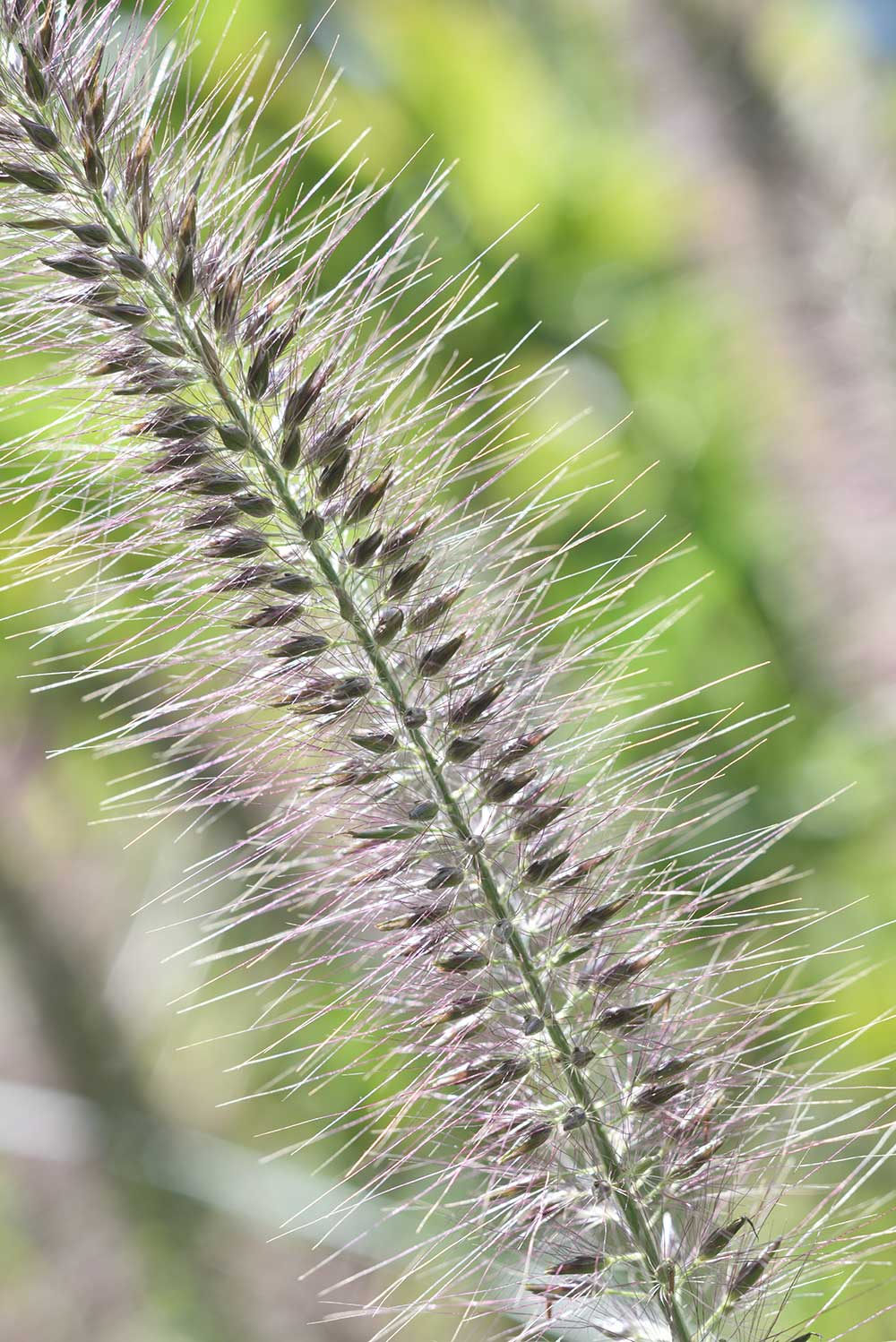
With Sample 7, I got even closer to my subject, capturing it at a magnification just over 1/2x. I was a little worried about focus, so I stopped the aperture down to f/8 for a photo in which the brightness of the partially backlit ears is beautifully expressed. Certainly, one of the most appealing aspects of close-up photography is the ability to reproduce that which is not readily visible to the naked eye. Samples 4 through 7 reproduce beautiful natural structures that the human eye cannot easily see in a clear and straightforward manner. One of the most useful and beneficial aspects of EL-Nikkor lenses is the superior resolution they exhibit with shooting at close distances.
When I began working at Nikon, the designer of the EL-Nikkor 80mm f/5.6N was working at Tochigi Nikon. He later returned to optical design and designed specialty lenses. Even now, I can picture him at the smoking area, quietly considering plans for the lens he was currently designing with a cigarette hanging from his lips. If my young self were to pass by at such times, he would call me over, "Mr. Ohshita, Mr. Ohshita! What do you think of this lens I'm working on?" I would respond with a comment like, "The structure here seems a little odd," and he would agree, "You're right. I don't like that either. Thank you!" and return to work.
Thinking about it now, I'm quite sure that he wasn't really asking for my opinion, but rather using conversation with me as a way to organize his own thoughts. Or, perhaps he wanted to show me the depth and breadth of lens design by sharing designs for a variety of non-photographic lenses.
If we look at Figure 1, the structure of the EL-Nikkor 80mm f/5.6N seems completely symmetrical with the same elements mirrored on either side of the aperture. However, a perfectly symmetrical design would result in aberration at the standard 5xmagnification. This means that even with a symmetrical structure, some of that symmetry must be taken away. Of the six lens elements utilized by this lens, two sets are made up of the same lens elements.
Symmetry has partly been taken away and performance increased by changing the curvature of, and material used for, just two lens elements. I'm sure that Mr. Mori spent time alone at the smoking area, pondering plans with a cigarette dangling from his lips, while designing this lens as well. He probably came up with the idea of using the same elements at such times. These are the thoughts and memories that often come to my mind.

NIKKOR - The Thousand and One Nights
The history of Nikon cameras is also that of NIKKOR lenses. This serial story features fascinating tales of lens design and manufacture.

